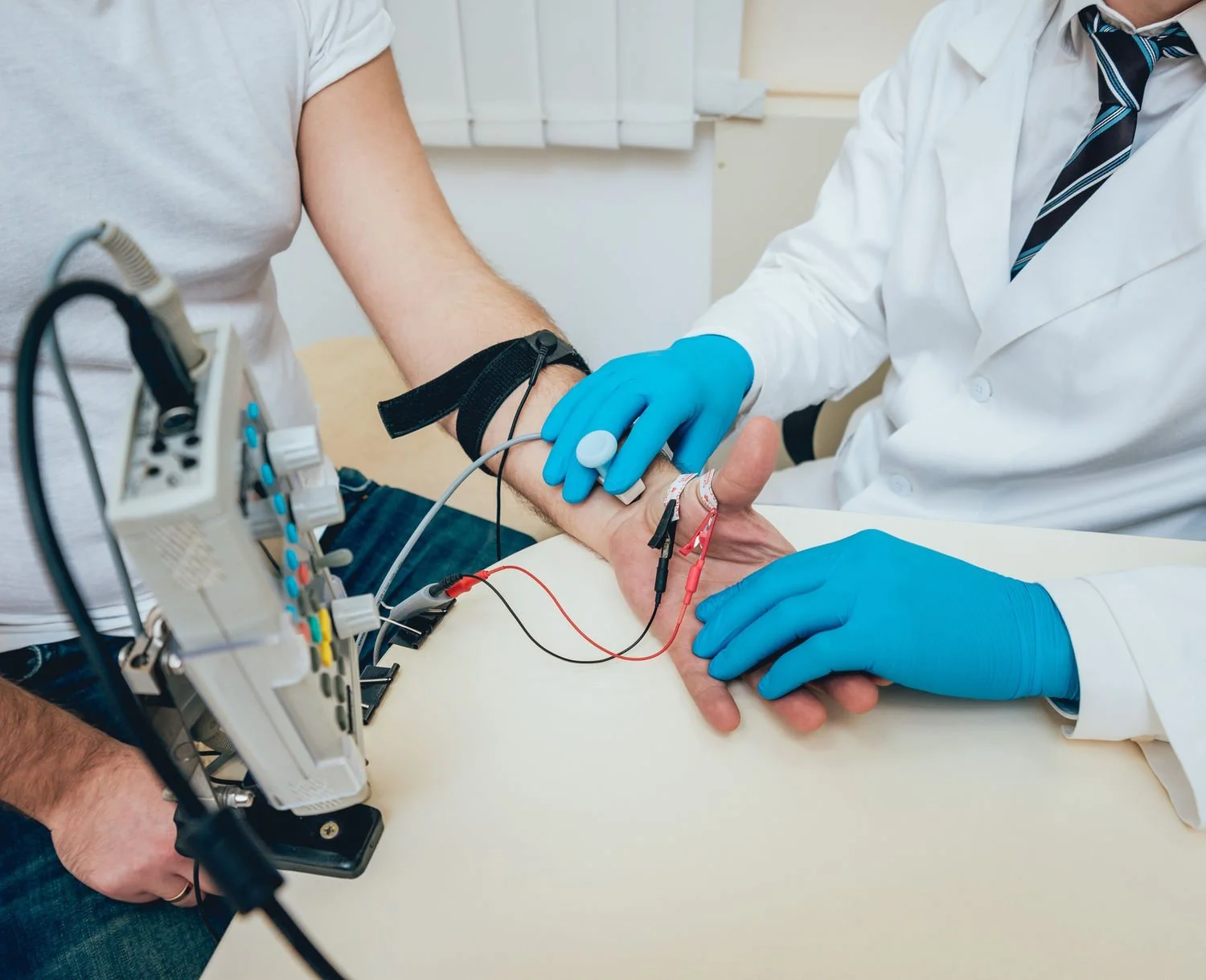
Electromyography (EMG) measures muscle response or electrical activity at the time of moving a muscle. The test is used to help detect nerve injury or muscle diseases such as carpal tunnel syndrome, a pinched spinal nerve, peripheral neuropathy, myositis, or amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS). The presence or absence of injury can be helpful in determining further treatment.
The most common symptoms that call for an EMG test include:
Numbness
Tingling
Muscle weakness
Radiating Back Pain
Cramping
If you need to get an EMG test, the specialist team at Neurology New South Wales specialists will schedule your testing and perform it in a safe environment. During the test, one or more small needles i.e., electrodes are inserted into the muscle. The electrical activity picked up by the electrodes is then displayed on the monitor that displays electrical activity in the form of waves. An audio amplifier is used so the activity can be heard, which is often noisy. EMG measures the electrical activity of muscles during rest, slight contraction and forceful contraction.
EMG Tests Sydney
EMG tests provide data about how the muscles and nerves function. The tests add valuable information to what your doctor already knows from your history, physical exam, imaging scans, and it is often an adjunct to nerve conduction testing. The results of the EMG test can reveal nerve dysfunction, muscle dysfunction or problems with the communication between the muscles and nerves.
EMG tests are low-risk, and complications are rare. People react differently to EMGs. You may experience some temporary discomfort, or minor soreness or bruising where the needle electrode was inserted into your muscle. This bruising should fade within several days. If it persists, you should contact your general practitioner. It is important that if you are on a blood thinner to mention this to the specialist performing the EMG before testing begins. Certain blood thinners increase the chance of bleeding when the small needles are inserted into muscles. Although this is mostly a precaution it is valuable information for specialists to know when performing the test.